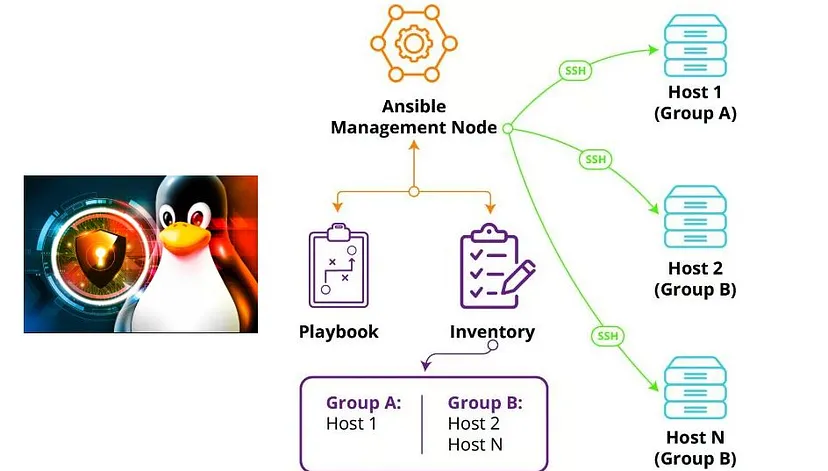






Ansible is an open source IT automation engine that automates provisioning, configuration management, application deployment, orchestration, and many other IT processes. It is free to use, and the project benefits from the experience and intelligence of its thousands of contributors. What We Did In this article, we covered essential practices for hardening both the operating system and SSH configurations to enhance security. Ansible Code Structuring Organized our Ansible playbooks and roles for streamlined configuration management. Established a clear structure to facilitate scalability and reusability of automation code. Operating System Hardening Key steps for securing the OS, including system updates, disabling unnecessary services, and securing system configurations. SSH Hardening Configurations to strengthen SSH security, such as limiting access, enforcing strong authentication, and other best practices. We want to run OS hardening on Server01 from DesktopTest ubuntu
At first we must install ansible on the DesktopTest :
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ansible
ansible --version
Note : python must be installed at any linux and consider that we have one linux for source (ansible management node) where the ansible is installed on it and one or many linux for destination that must be harden by ansible.
Important : management node must can ssh to any destination node passwordlesslly.
for this reason, we generate a ssh key on management node and copy it to any destination nodes.
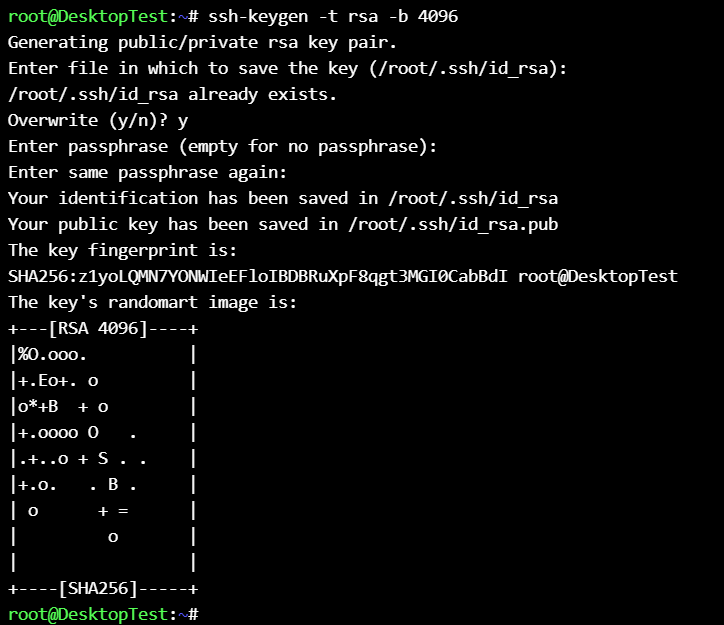
on management node :
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
Generated keys at /root/.ssh :
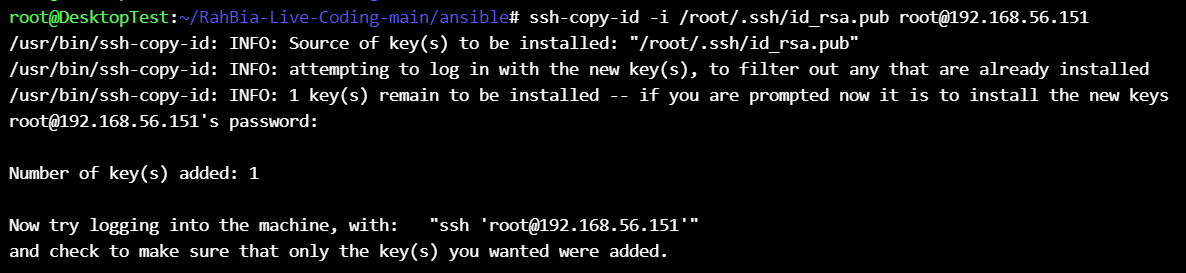
Copy the public key (id_rsa.pub) to other nodes :
ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@192.168.56.151
Check the public key on management and destination node …
management node (DesktopTest) :
destination node (Server01) :
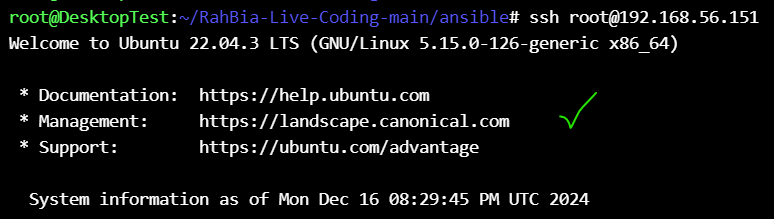
Test the ssh login passwordlesslly :
ssh root@192.168.56.151
We use some of the rules from the Link ansible-collection-hardening.
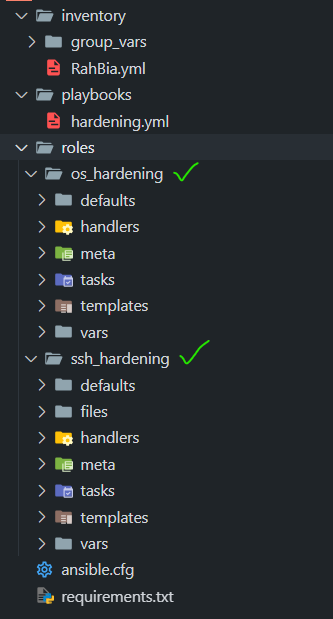
then check the ansible project and files at management node :
All the project files has presented at my github.
files on management node :
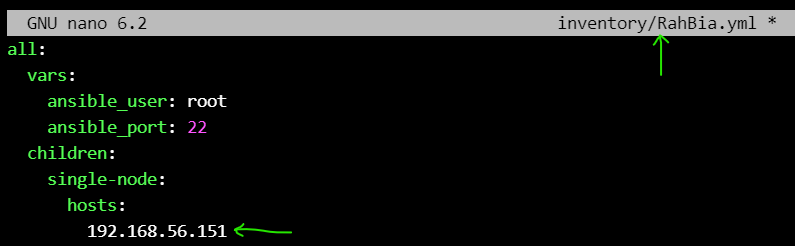
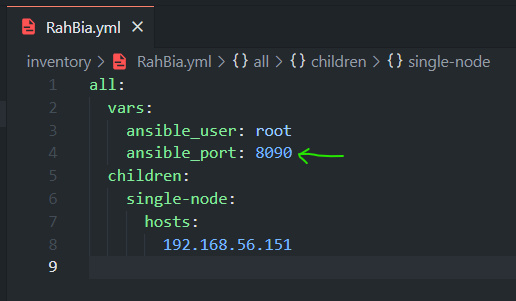
Edit the inventory file based on destination node(s) :
all:
vars:
ansible_user: root
ansible_port: 22
children:
single-node:
hosts:
192.168.56.151
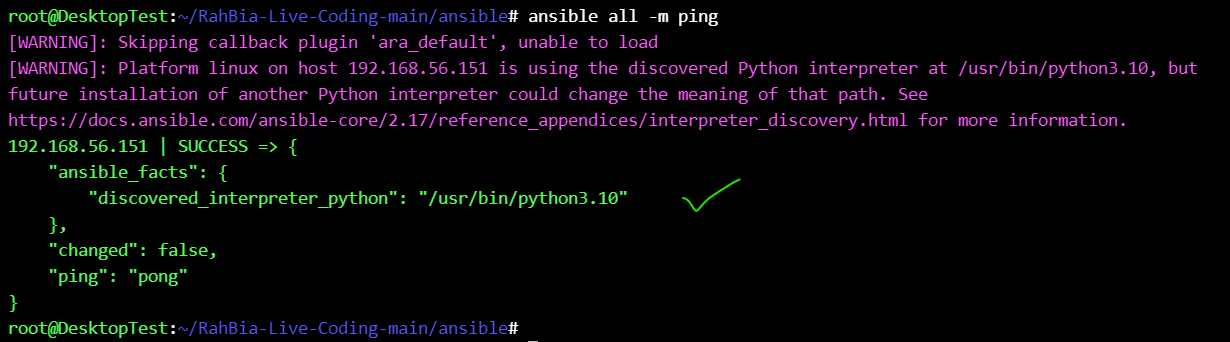
then ping all destination host(s) to be ok before running the ansible playbooks :
ansible all -m ping
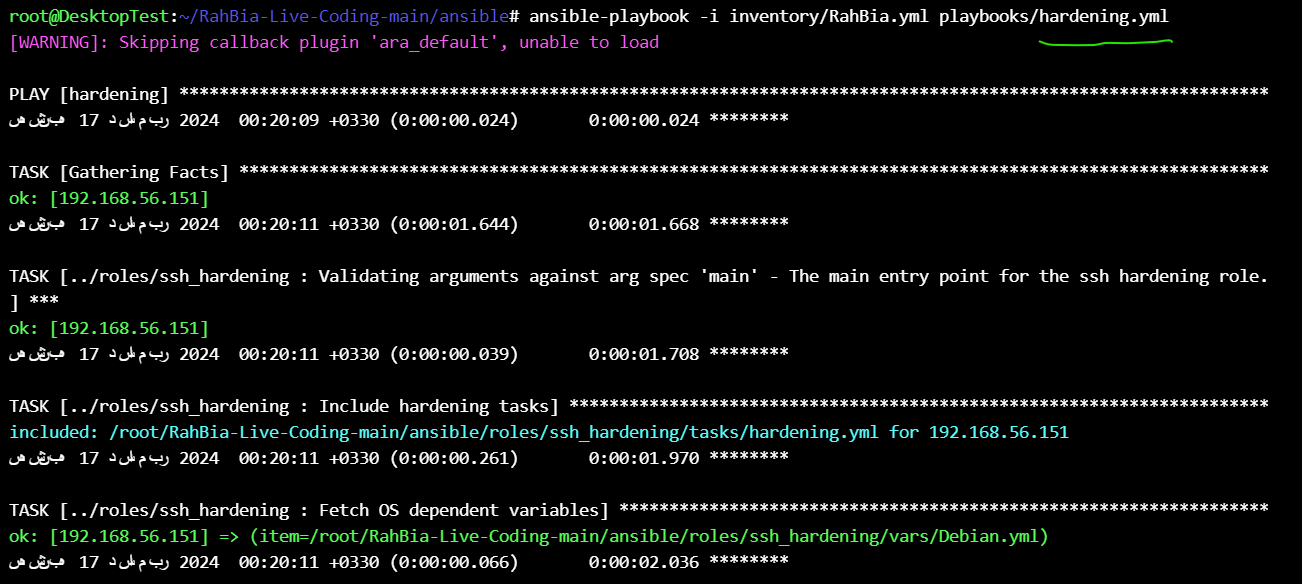
then run the playbook :
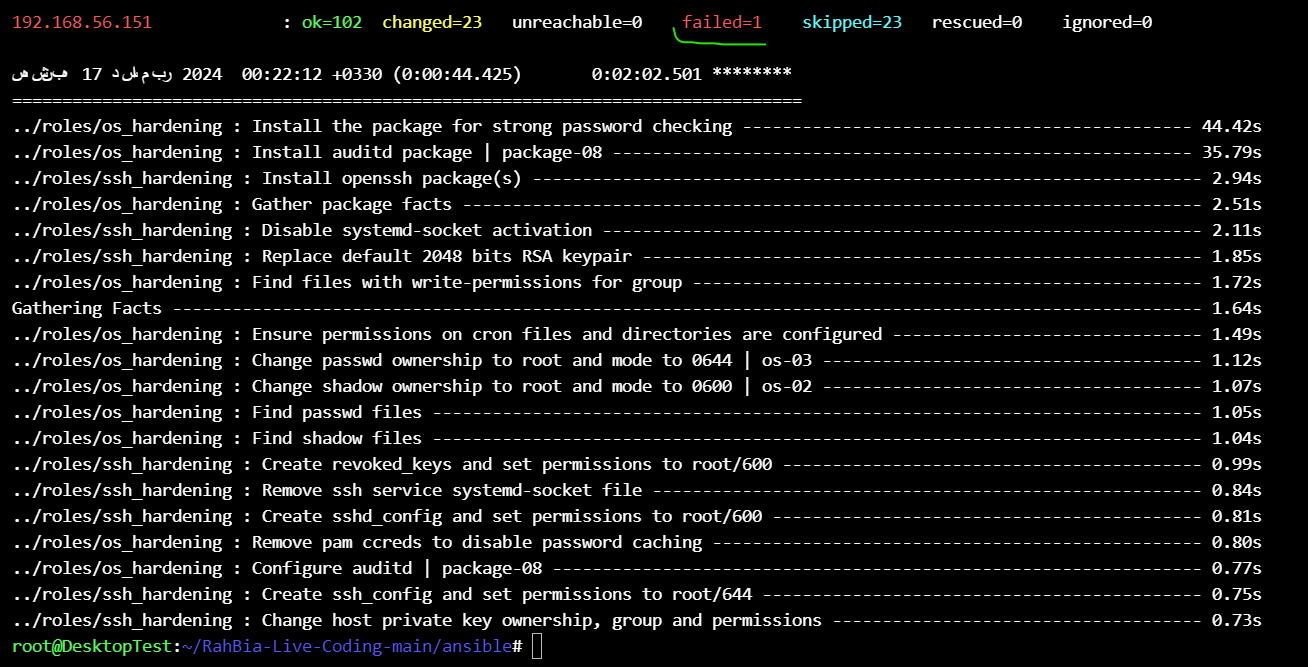
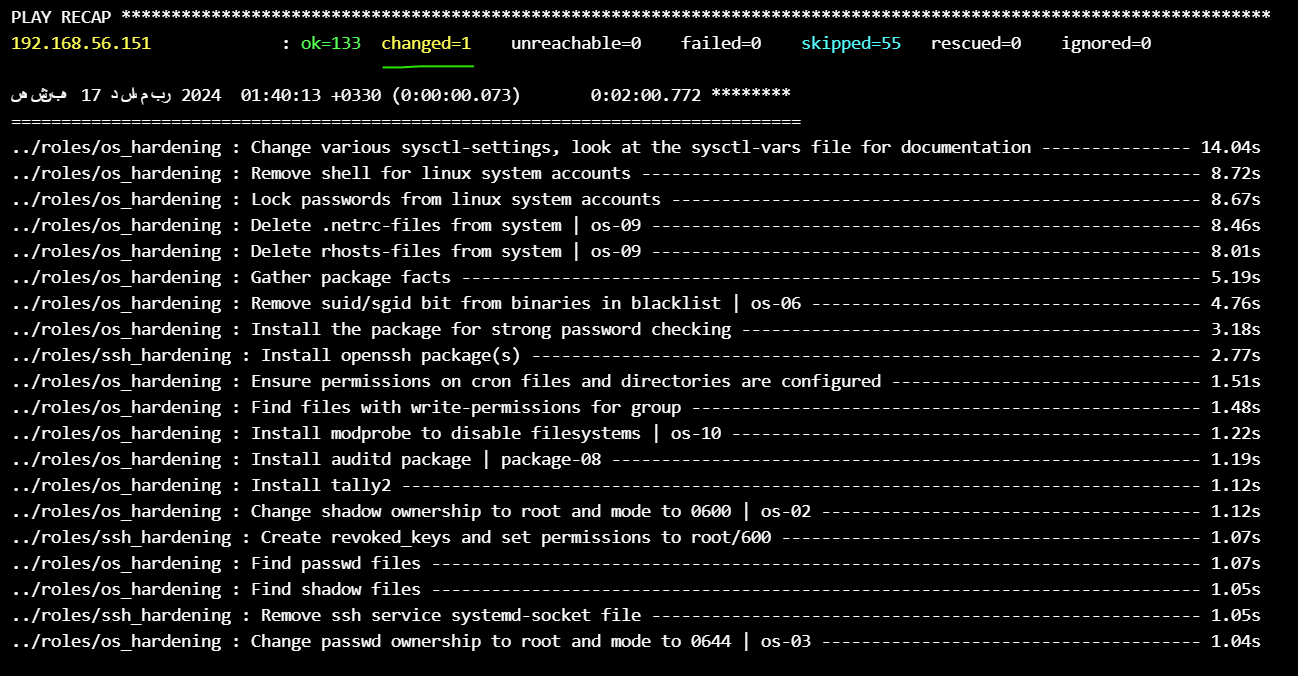
ansible-playbook -i inventory/RahBia.yml playbooks/hardening.yml
if any error happens, check and correct it and run the playbook again
Note : ansible process is idempotent, an idempotent operation is one that has no additional effect if it is called more than once with the same input parameters.
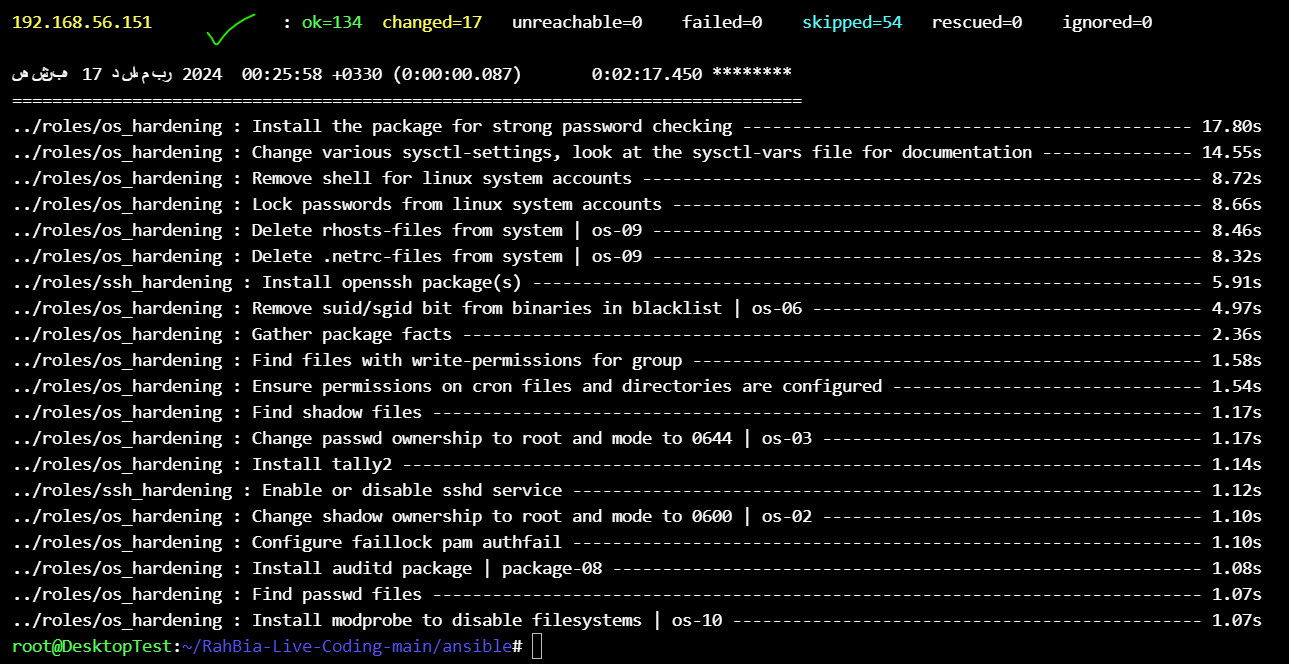
ansible-playbook -i inventory/RahBia.yml playbooks/hardening.yml
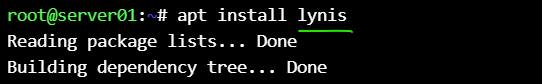
for checking the hardening, install lynis on destination nodes :
apt install lynis
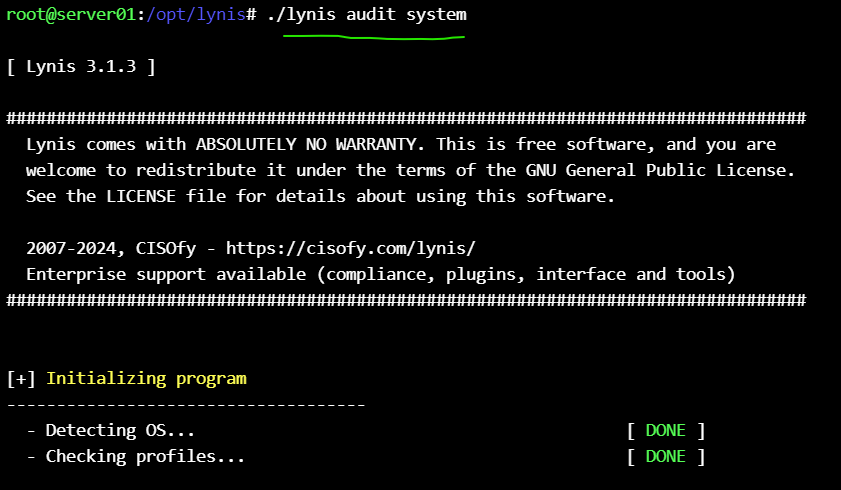
run the lynis to audit the node :
./lynis audit system
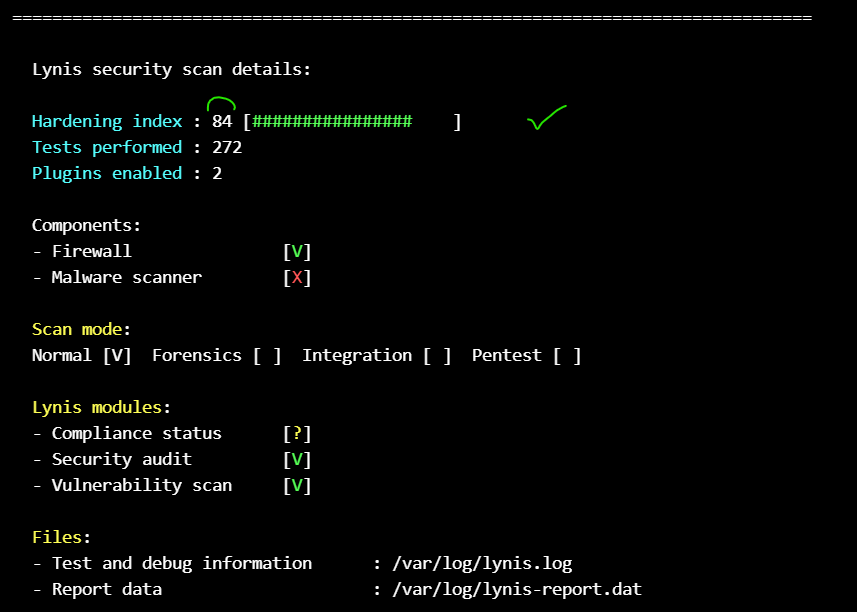
at final, check the grade (84 % at our case) :
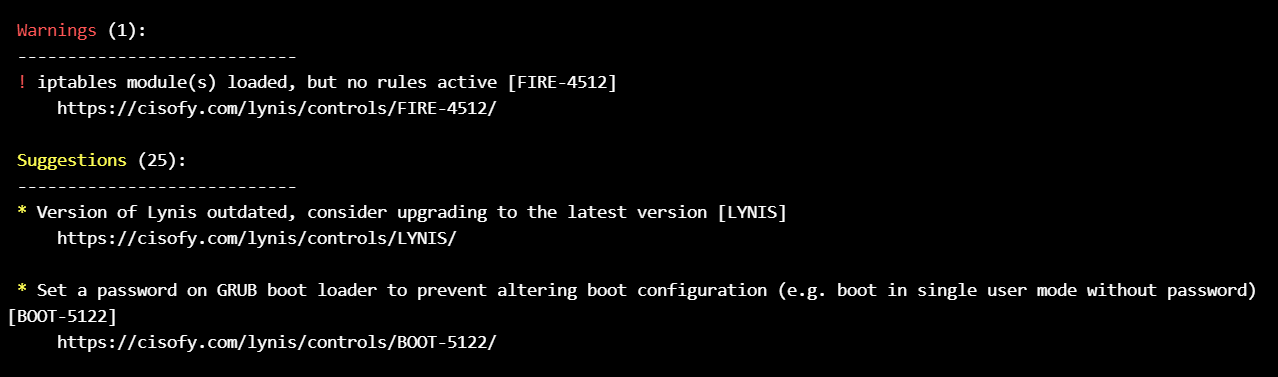
and check any warnings and suggestions :
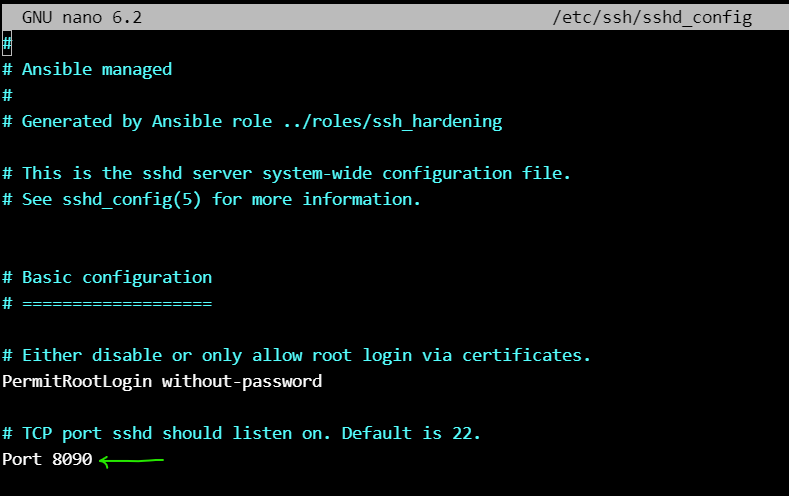
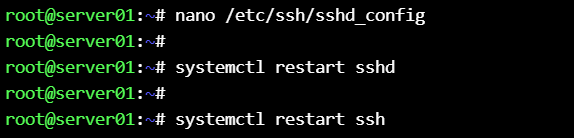
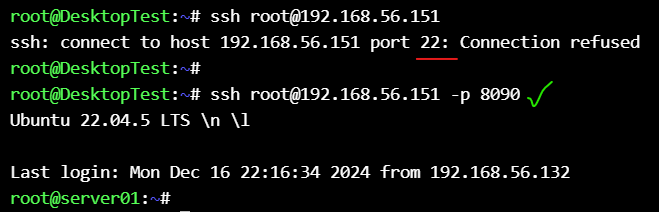
you can change the destination ssh port (to 8090 in our case) and run the playbook with that port :
ansible-playbook -i inventory/RahBia.yml playbooks/hardening.yml
ssh root@192.168.56.151 -p 8090
ss -nltp | grep ssh
 https://github.com/kayvansol/AnsibleHardening
https://github.com/kayvansol/AnsibleHardening























Leave a Reply